Scientists Are Rethinking Space-Time As We Know It

NASA’s latest findings are turning what we thought we knew about the universe completely upside down. A recent mission, which initially aimed to map distant celestial bodies, ended up revealing bizarre behavior in the structure of space-time. Data showed unusual gravitational patterns and time distortions that didn’t match anything in the models scientists have trusted for decades. If that sounds like science fiction, you’re not alone. Researchers themselves were stunned by the implications.
It’s as though the fabric of space is bending and stretching in ways we’ve never measured before. These phenomena suggest there could be unknown dimensions or even cracks in the cosmic structure where time doesn’t behave the way it should. The scientific world is cautiously calling it a breakthrough, and many agree this could lead to a new era in physics. For now, space-time is no longer a passive backdrop. It’s alive with activity—and mystery.
The Discovery Is Strengthening Belief in a Multiverse
For years, the multiverse idea was mainly reserved for movies and late-night theories. But NASA’s new discovery has sparked a shift in how seriously the concept is being taken in scientific circles. While observing background radiation in deep space, researchers noticed repeating anomalies—patterns that seem out of place in our known universe. Some scientists believe we may be seeing physical evidence that points to a neighboring universe or dimension interacting with ours.
These anomalies don’t just appear once and vanish. They’re consistent, recurring, and stubbornly resistant to traditional explanations. The data feels like a cosmic breadcrumb trail, suggesting that our universe may be just one bubble in a vast foam of realities. Experts are now exploring the possibility that our universe isn’t a lonely cosmic island, but part of a much bigger structure—something more complex and interconnected than we ever imagined.
We Might Have Spotted the First Signs of Life-Supporting Exoplanets
NASA’s advanced telescopes have zeroed in on several distant exoplanets, and the early signs are incredibly promising. These planets are located in what scientists call the “habitable zone,” where conditions are just right for liquid water to exist. But what’s truly fascinating is that their atmospheres contain trace elements often associated with life—like water vapor, oxygen, and even methane, which on Earth is a biological byproduct.
It’s not just the chemical makeup that’s exciting researchers. These exoplanets also show signs of having stable orbits and possibly even magnetic fields—two critical features for protecting life from harmful cosmic radiation. While we haven’t found alien life just yet, the discovery is a giant leap forward. It’s giving scientists hope that Earth-like conditions may not be as rare as once thought. And that opens up a future filled with thrilling possibilities.
Dark Energy Is Acting Stranger Than Expected
Dark energy has always been one of the universe’s most mysterious forces. It’s the invisible pressure pushing galaxies apart at an accelerating rate. But NASA’s latest measurements reveal that this energy doesn’t act as uniformly as once believed. Instead of a steady, constant force, dark energy appears to vary across different regions of space. This inconsistency is challenging everything scientists thought they knew about how the cosmos works.
If dark energy isn’t consistent, it could mean we’re missing an essential ingredient in our understanding of the universe. Some experts believe there might be entirely new physics at play—forces or particles that haven’t been detected yet. Others suggest dark energy might evolve over time or interact with matter in ways we don’t yet understand. Either way, it’s a scientific curveball that’s forcing researchers to rethink the ultimate fate of the universe and how we fit into it.
Gravitational Waves Are Revealing Invisible Structures
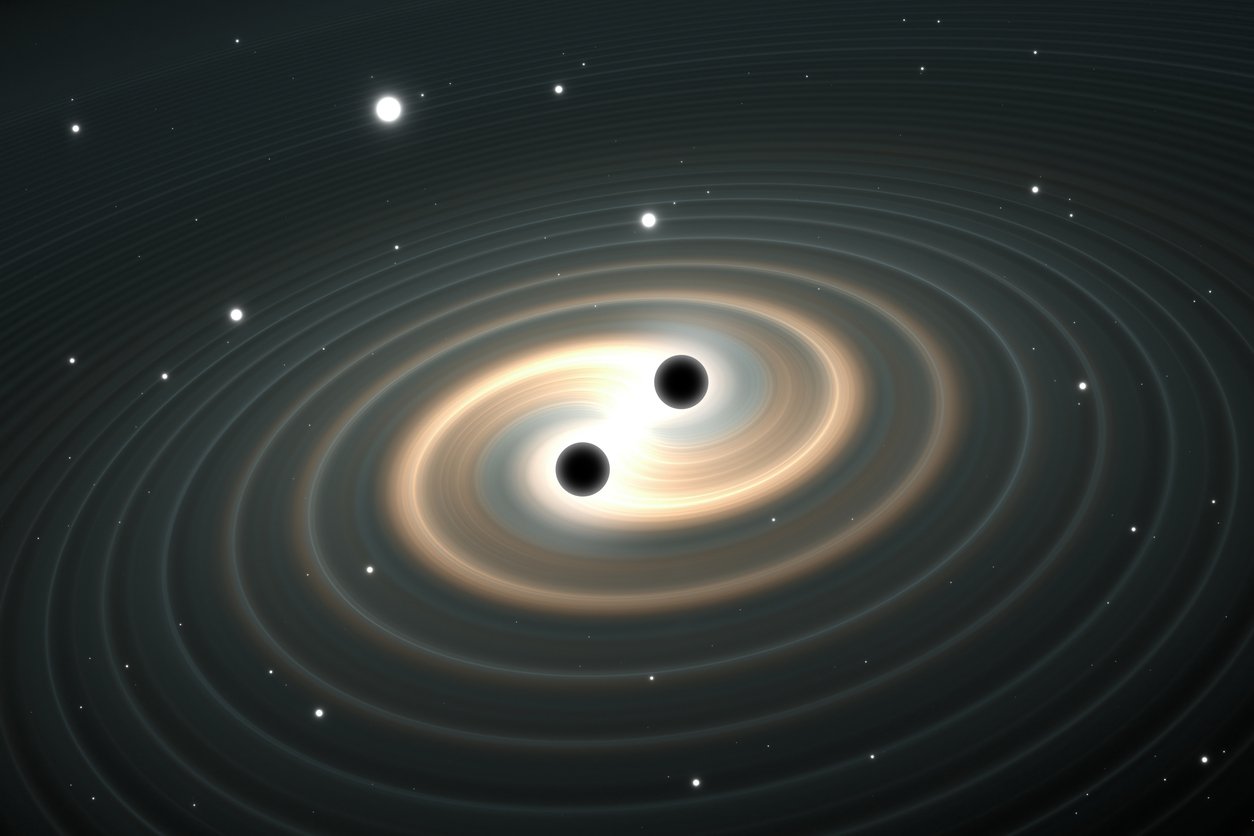
Gravitational waves, those tiny ripples in the fabric of space-time have opened an entirely new window into the universe. NASA’s latest discovery captured an unusual pattern of these waves that suggests the presence of massive, unseen structures in the far reaches of space. These aren’t black holes or neutron stars like the ones we’ve detected before. They’re something different. Something bigger. Something that doesn’t emit light, but definitely has mass—and a lot of it.
This observation hints that there might be colossal cosmic objects or even ancient remnants of the early universe hiding in plain sight. Think of it like watching waves ripple across a pond without ever seeing what caused the splash. Scientists are now using gravitational wave data to map out these “ghost” structures, and it’s changing our entire approach to cosmic cartography. The invisible is becoming visible, and it’s reshaping how we understand the architecture of the universe.
A Strange Cold Spot May Be a Portal to Another Universe
For a while now, astronomers have been puzzled by a particularly strange feature in the cosmic microwave background—a cold spot that’s significantly cooler than the surrounding space. With NASA’s recent advancements in telescope resolution, this cold spot is back in the spotlight, and the latest data suggests it may not be a fluke at all. Some scientists believe it could be the result of a cosmic bruise—where our universe may have bumped into another one.
This kind of overlap wouldn’t just support the multiverse theory. It would provide one of the most tangible pieces of evidence we’ve ever had. The area around this cold spot behaves differently in terms of radiation and particle distribution, and that irregularity doesn’t match anything in current cosmological models. If further studies confirm its uniqueness, it could be one of the first physical hints that we’re not alone in the grander multiverse.
Time May Flow Differently in Distant Galaxies
One of the most shocking implications from NASA’s new data is the possibility that time itself might not be as universal as we think. Instruments aboard their latest probe measured strange discrepancies in time dilation when observing distant galaxies. These variations weren’t just minor delays—they were enough to suggest that time could be flowing faster or slower depending on where you are in the universe.
This isn’t a small tweak to the theory of relativity. It’s a potential game-changer. The idea that the speed of time could vary across the cosmos means our assumptions about aging stars, cosmic expansion, and even the beginning of the universe may need rethinking. Some researchers are beginning to wonder if there are “pockets” in space where time operates by a different set of rules altogether. It’s a concept that sounds surreal, but it’s being taken seriously because the math and measurements are lining up.
Hidden Dimensions May Be Lurking in Plain Sight
NASA’s recent exploration of high-energy cosmic rays has opened up a stunning possibility—hidden dimensions may exist, and they might be far more accessible than previously believed. While probing energetic particles beyond our galaxy, researchers detected odd behavior that didn’t match the three spatial dimensions we’re familiar with. The particles appeared to “leak” in patterns that could only be explained by additional dimensions affecting their motion.
These aren’t parallel universes in the sci-fi sense but actual spatial dimensions that could exist alongside the ones we perceive. Scientists have long theorized their existence through string theory, but now, the data may finally be catching up. If confirmed, it would mean the universe is far more layered than we imagined—like a cosmic lasagna with hidden folds influencing everything from gravity to light. It’s not just abstract math anymore. It’s the start of a very real, very wild new chapter in physics.
Alien Megastructures Are Back on the Table

In one of the more jaw-dropping turns, NASA’s latest scans picked up unusual light fluctuations around a distant star system. Initially dismissed as equipment errors or asteroid interference, these signals have now persisted through multiple observations, suggesting something massive and structured is orbiting the star. Naturally, the idea of an “alien megastructure” sounds outrageous—but not impossible. The data shows a level of regularity and size that natural phenomena like planets or dust clouds don’t quite explain.
Experts are careful not to jump to conclusions, but some are now revisiting old theories about Dyson Spheres—hypothetical structures built to harness a star’s energy. While it’s a long shot, the behavior of light and shadow in that region is too peculiar to ignore. If it’s not an alien-built object, then it’s a cosmic event unlike any we’ve seen before. Either way, it’s a mystery that forces us to consider just how much more there could be out there—watching, waiting, or building.
